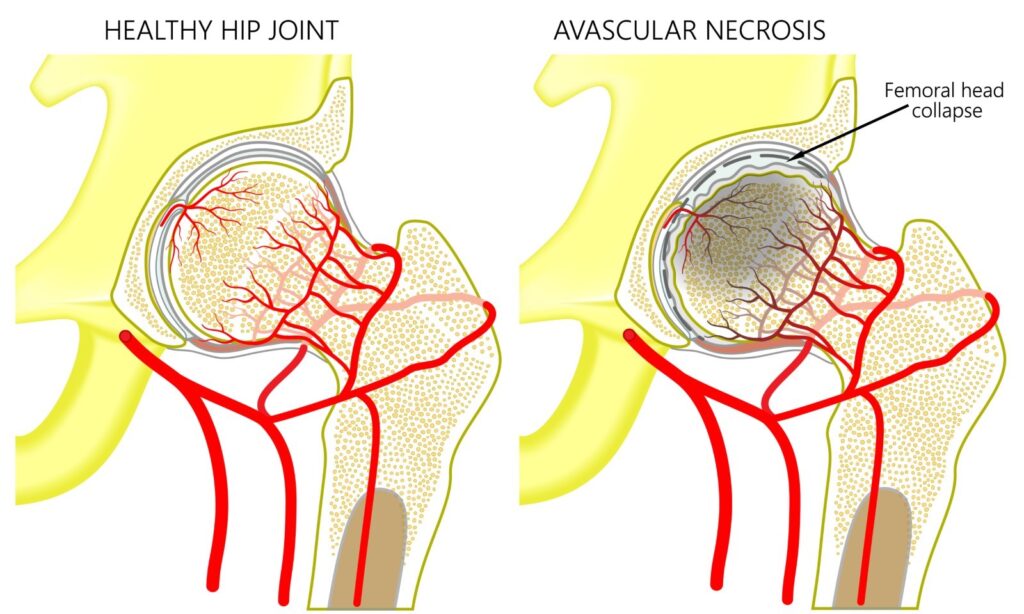
What is Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of the Hip?
Avascular Necrosis, often called AVN, refers to the death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply. When this happens in the hip, it can cause serious issues. The hip joint is where the thigh bone meets the pelvis. If the blood flow to the “ball” part of this joint stops or reduces, the tissue starts to die. This leads to a weakened joint and can eventually cause the joint to collapse.
Imagine this: the ball of the thigh bone needs blood like a tree needs water. When the water stops, the tree starts wilting. Similarly, the ball of the thigh bone starts to crumble when blood supply ends. This is a simple way to picture AVN of the hip.
People often misunderstand AVN. Some think it’s just about arthritis or simple wear and tear due to age. In reality, AVN results from something stopping the blood from reaching the joint. The consequences of AVN are more severe and need specific attention. Unlike typical joint problems, AVN can worsen quickly if not attended to early. Understanding this condition helps in recognizing symptoms soon and seeking help.
The Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis of AVN Hip
Numerous factors can lead to AVN of the hip. Here are some prominent causes:
- Lifestyle choices: Heavy drinking, smoking, or taking steroids can increase the risk.
- Medical conditions: Diseases like diabetes or lupus can affect the blood supply.
- Injuries: Hip injuries or fractures might disrupt blood flow to the joint.
- Genetic Factors: Sometimes, family history can play a role.
Recognizing AVN hip symptoms is crucial. This condition often starts with persistent pain in the hip. You might feel discomfort during movement or when lying down. Over time, the pain becomes constant, affecting daily activities. Another symptom is stiffness or limited motion in the hip joint. Imagine trying to move your hip, but it feels stuck or achy more than usual.
Early detection is key. Noticing these signs earlier can prevent severe damage. AVN hip diagnosis involves some simple tests. Doctors often start with X-rays to see changes in bone structure. If further detail is needed, they may use MRI or CT scans. These tests provide a clearer picture of what’s happening inside the hip joint.
Doctors play a critical role in diagnosing AVN of the hip. They use these tests to confirm whether AVN is causing the discomfort. Early diagnosis can determine how treatment plans are shaped, making timely intervention possible.
Exploring Treatment Options and Recovery Paths for AVN of the Hip
When it comes to AVN hip treatment options, there’s a mix of non-surgical and surgical routes. For less severe cases, lifestyle changes and physiotherapy are common choices:
- Lifestyle adjustments: Reducing or stopping alcohol and smoking can slow progression.
- Weight management: Keeping a healthy weight lessens stress on the hip.
- Physiotherapy: Exercises improve mobility and reduce pain.
For advanced AVN of the hip cases, surgery might be necessary. Here are some common surgical interventions:
- Core decompression: This procedure involves drilling into the bone to improve blood flow.
- Hip replacement: When the joint is significantly damaged, replacing it with an artificial one might be recommended.
Recently, there have been medical advances in AVN treatment. New techniques focus on enhancing blood supply and using biological methods to heal affected areas. These advancements can help improve recovery and patient outcome.
Recovery from AVN hip procedures varies. However, a committed rehabilitation plan is vital. Patients are advised to follow specific post-surgery exercises. Sticking to these routines enhances healing and brings back mobility. Consistency in rehab plans is key to seeing the best results.
Preventive Measures and Future Outlook for AVN of the Hip
Prevention is always better. To reduce the risk of AVN, consider some healthy lifestyle tips:
- Regular check-ups: Routine medical tests can catch issues early.
- Balanced lifestyle: Moderate drinking, avoiding steroids unless prescribed, and maintaining a healthy weight go a long way.
Educating patients on how AVN develops and progresses is also crucial. Early knowledge acts as a preventative tool.
Research continuously improves AVN hip treatment strategies. Technology plays a role in prevention and early detection, which are essential elements in managing this condition.
In conclusion, while AVN of the hip poses challenges, continuous research and dedicated treatment approaches support better management. The future of treating and managing AVN seems promising with ongoing advances in medical science.