Arthritis Management
Arthritis Management
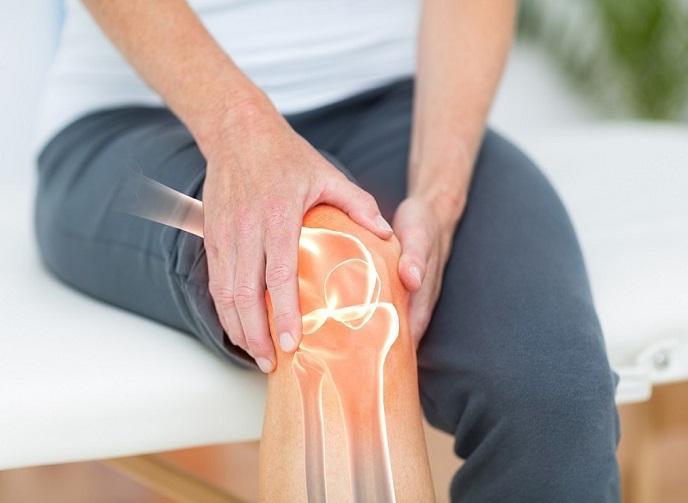
Arthritis refers to the inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. It can affect any joint but is most common in the knees, hips, hands, and spine. The two most prevalent forms of arthritis are osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). While arthritis cannot be cured, effective management strategies can help reduce symptoms, improve joint function, and enhance the quality of life.
Physical Therapy:
- A customized physical therapy program helps strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, improve mobility, and reduce stiffness. Occupational therapy may also assist with joint protection techniques and assistive devices to make daily tasks easier.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on weight-bearing joints, particularly in OA of the knee and hip.
- Exercise: Low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can improve joint flexibility, muscle strength, and overall function.
- Diet: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants) may help manage symptoms.
Surgical Treatment:
- When conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary. Options include:
- Joint Replacement Surgery: Common for advanced OA, especially in the hip and knee, where damaged joints are replaced with artificial prostheses.
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to remove damaged tissue or repair joint structures.
- Joint Fusion: In severe cases, fusion of the joint may be performed to relieve pain and stabilize the joint.
- When conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary. Options include:
Arthritis management is personalized, focusing on symptom relief, functional improvement, and preventing further joint damage. Early intervention and a combination of medical, physical, and lifestyle strategies can significantly improve outcomes and allow individuals to maintain an active lifestyle.