Shoulder Arthroscopy
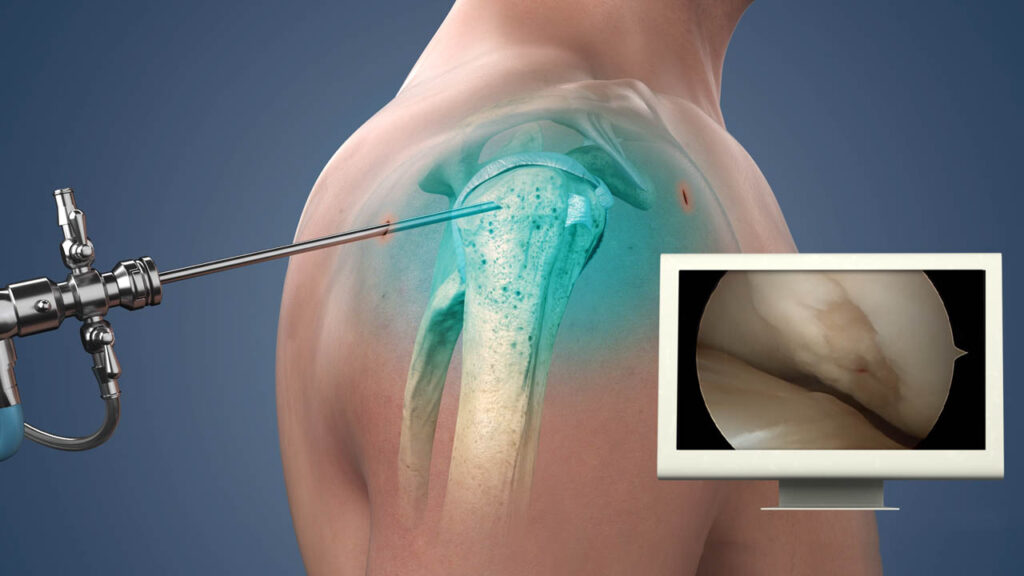
Shoulder Arthroscopy
Shoulder arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat a variety of shoulder conditions. It involves making small incisions through which a tiny camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments are inserted into the shoulder joint. The camera provides real-time images of the inside of the joint, allowing the surgeon to accurately identify the source of the problem and perform necessary repairs.
Common conditions treated with shoulder arthroscopy include rotator cuff tears, shoulder instability, labral tears, impingement syndrome, and shoulder arthritis.
The procedure can be used to remove damaged tissue, repair torn ligaments or tendons, or remove bone spurs that may be causing pain.
The advantages of shoulder arthroscopy over traditional open surgery include smaller incisions, reduced scarring, faster recovery, and a lower risk of infection. The procedure typically takes between 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the complexity of the issue. It is performed under general or regional anesthesia.
After surgery, rehabilitation is key to restoring function. Physical therapy helps strengthen the shoulder, improve range of motion, and reduce stiffness. While recovery time varies depending on the procedure performed, most patients experience significant improvements in pain relief and shoulder function. Shoulder arthroscopy allows for effective treatment with minimal disruption to the surrounding tissues, enabling patients to return to their daily activities or sports with a quicker recovery time.